Dr. Susana L. Gallardo
Lecture notes: Sex & Gender
rev. 8/2016
What's the difference between sex & gender?
What are "traditional" ideas of gender?
What are different theories of gender?
Where do we see ideas of gender changing?
What does it mean to "do gender"? Why does that matter?
Sex
- A biological, physiological category.
- Scientifically verifiable.
- A set of characteristics by which we are assigned to one of two sexes at birth.
- Static
Sex markers 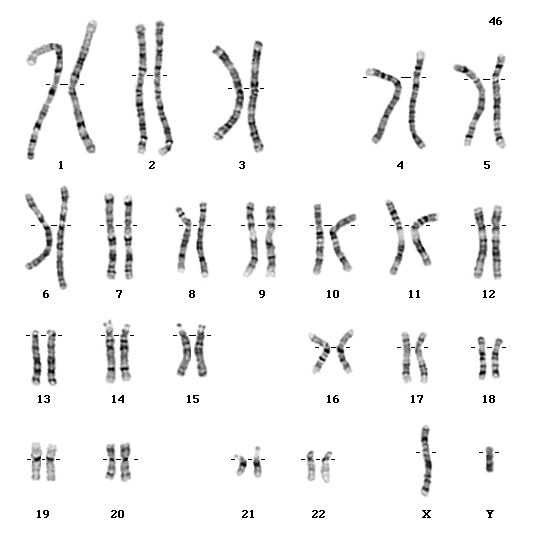 include
include
- Chromosomes: XX XY.
- Genitals
- hormones
- physical size, frame
- body hair, breast size, Adam's apple, voice
Sex is a primary, fundamental organizing category in our society—
bathrooms, institutions, education, marriage, etc.
So important that we surgically mutilate newborn babies that do not fit our expectations.
Gender
- "The way you identify"
- the two social roles our society typically associates with physiological sex.
- Stereotyped characteristics ascribed to sex, the ideas we express with the terms “masculine” and “feminine.” Examples?
- the meaning of "sex" within a particular cultural/historical context
- Extends far beyond physiological sex to inanimate objects
- Dynamic
Gender markers include:
- clothes
- colors
- hairstyle
- activity (watching baby, loading trucks)
- earrings/jewelry
- body language
- occupation
- Behaviors: walk, hug, cry, sit, talk
Notice: Body hair might be a sex characteristic, but how we deal with it is gendered.
Gender is hard to identify because it feels “natural”:
What is natural? What is biological? What is cultural?
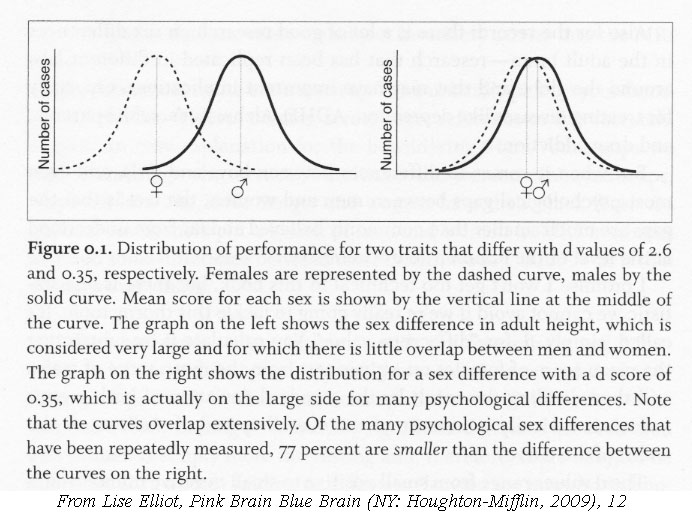
Gender is Dynamic – constantly changing
“Doing gender” - we do/perform our gender everyday.
Agency - our own experience, model, teacher...
Gender Socialization - colors
– A lifelong process by which we learn and integrate ideas of gender, differing by age, environment, culture, etc.
Where do we learn gender?
- Parents, family, siblings
- School
- Religion
- Media
- Friends/peers.
Theories of Gender - why are men and women different?
Essentialism -
- Gender is inherent, an essential difference.
- Religious source: “God made us male and female” (did God?)
- Historically, a primary explanation, conflating sex and gender
- Increasingly disproven, yet remains overwhelmingly popular
Social constructionism
- Gender is created by culture and society.
- We learn to be girls/boys.
- Exists only inasmuch as we created it, somewhat arbitrary.
- Recent science, social science shifting away from essentialist toward social constructionist.
And yet, this model is simplistic -
Some of the most interesting work in between the two poles–brain differences because of social behavior, etc. Where does biology end and gender begin?
How does the brain process differential gender behavior?
The math/science conundrum
Terms to know
- sex
- sex markers
- gender
- gender markers
- agency
- gender socialization
- essentialism
- social constructionism
 include
include  include
include 